
« The Enneagram is, in its most abstract form, a universal mandala of the self – a symbol of each one of us. »
– Don Richard Riso
The Enneagram offers us the possibility to change our perception of ourselves, to bring more meaning, awareness, kindness, and confidence to it. It helps us objectively observe ourselves, understand our origins, realize our full potential, and progress towards a better life and a better world. It’s a tool for self-observation that allows us to see beyond our masks and appearances.
Want to discover the Enneagram?
Let us introduce you to our Introductory and Deepening Modules!
A first module to start your learning of the Enneagram and its enneatypes!
And a second one to delve deeper into this initial knowledge, to dig more deeply into your enneatype!

Module 1: Introduction Day
“Discovery of the Enneagram and personality profiles”
The Enneagram can be used to help people better understand themselves and others, by providing a framework to explore their deep motivations, habits, and compulsions. Quests and aspirations, motivations and avoidances, fears and desires, defense mechanisms, and relational strategies… You’ll discover the 3 centers of intelligence, the main characteristics of the 9 points, and the possible paths of evolution.
OBJECTIVES?
– Understand the historical context of the Enneagram.
– Understand how the Enneagram works.
– Identify your personality profile among the 9 profiles and your dominant center of intelligence through introspective exercises, exchanges, and positioning.
– Understand different personalities and develop an open mind towards others.
– Understand the characteristics (strengths, areas of caution, motivations, fears, paths of evolution, etc.) of the 9 profiles and the 3 centers of intelligence (instinctive, emotional, mental).
Module 2: Deepening Weekend
Module 2 follows Module 1, which is the “Introduction Day” to the Enneagram, previously completed. This second module aims to explore more deeply the concepts and applications of the Enneagram.
During Module 2, you’ll go beyond the basics and the nine personality types of the Enneagram that you discovered in Module 1. You’ll delve deeper into understanding yourself and others by exploring deep motivations, desires, defense mechanisms, and specific relational strategies for each type. Moreover, you’ll explore the three centers of intelligence, which are a fundamental part of the Enneagram.
OBJECTIVES?
– Become aware of defense mechanisms and childhood-developed wounds to understand how our personality was constructed..
Individual Journey
Sometimes, participating in a module with others can be complicated because we all have different paces, desires, and needs. Immerse yourself in self-discovery through a personalized 1.5-hour journey dedicated to your Enneagram type. Explore the depths of your personality, understand your motivations, and discover how to maximize your potential through this ancient self-awareness method.
Study your behaviors and motivations to transform limiting patterns into growth opportunities. Embrace a holistic approach to better understand yourself and relate to others.
What to expect:
– Intuitive Session : A 1.5-hour one-on-one session where we’ll explore your Enneagram type, its implications, and how it influences your daily actions.
– Personalized Analysise : Decipher your type, your typical reactions, and thinking patterns for a better self-understanding.
– Growth Strategies : Practical tools and advice to evolve towards a more balanced state and utilize your potential to the fullest.
A “brief” overview of the Enneagram! 👇
The term “Enneagram” comes from the Greek meaning “figure with 9 points,” with “ennea” meaning nine and “grammos” meaning figure or drawing. It’s an ancient system for understanding personality that has mystical origins. It’s believed to trace back to oral teachings transmitted by figures like Pythagoras and the Desert Fathers, further developed by Sufis like Evagrius Ponticus. The Enneagram figure is a nine-pointed star inscribed within a circle, formed by a six-pointed star inscribed within a triangle.
Introduced to the West in the 20th century by Georges Gurdjieff, a mystic and spiritual teacher, some historians and researchers suggest that the Enneagram might have origins predating Gurdjieff, influenced by mystical traditions such as Sufism, an esoteric tradition within Islam, as well as esoteric Christian and Jewish teachings.
In the 1970s in California, authors like Oscar Ichazo and Claudio Naranjo helped popularize the use of the Enneagram in modern psychology. They developed typologies of personality into nine distinct types based on this symbolic figure. This system provides insights to better understand ourselves and others, with nine archetypes to answer questions like « Who am I? », « Who is the other? », and « How can we better connect? ».
Today, the Enneagram is used in various fields such as psychology, personal development, relationship management, coaching, and even within certain spiritual circles to better understand individuals’ motivations, behaviors, and thought patterns, offering a powerful tool for self-development and self-awareness.
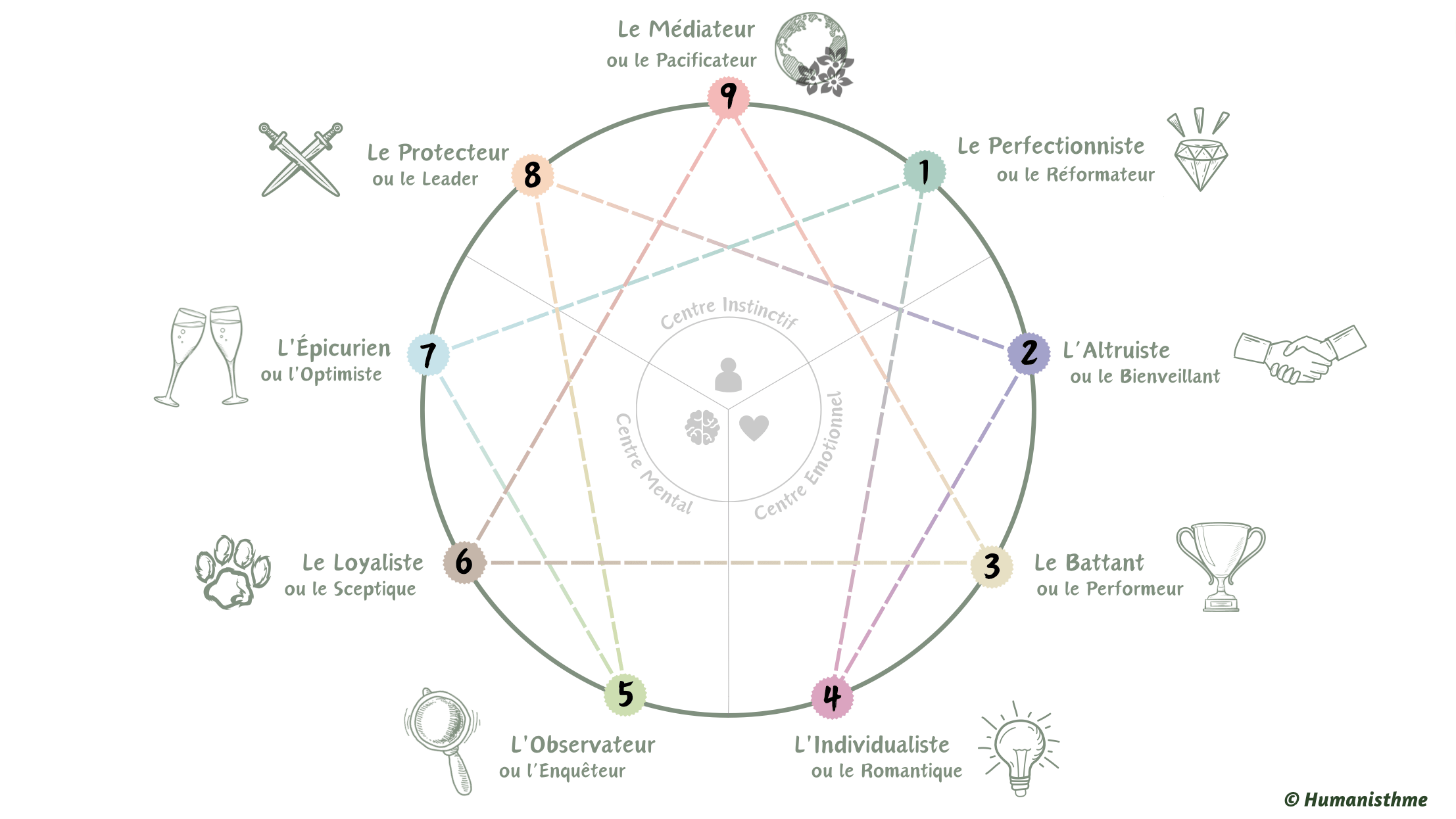
The Enneagram, an ancient geometric figure, represents three fundamental shapes: the circle (unity/wholeness), the triangle (triad/trinity), and the hexad (laws of seven). From the Greek “ennea” (ἐννέα = nine) and “gramma” (γράμμα = sign), it categorizes individuals into nine different personality types. Each archetype is represented by a number and a name, providing information about strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas for personal growth for each individual
The nine points of the Enneagram symbolize the strengths we possess, and the system helps us recognize and rebalance them. It is based on understanding personality through three axes: body, emotion, and mind
Each point represents a specific personality type with its own characteristics, motivations, fears, and tendencies. The lines connecting the points represent relationships between different types. Each type is connected to two other types by lines indicating specific dynamics: integration towards a healthy type (growth arrow) and disintegration towards a stressed type (stress arrow)
Here’s an explanation of the nine points and their symbolic meanings:

Check out the “Nine Types” section for more information!
These nine types offer insight into the different motivations, fears, and behavioral tendencies underlying human personality from the perspective of the Enneagram. Each individual may exhibit aspects of several types, but one type typically predominates in each person’s personality structure.

- Type 1 – The Perfectionist (or the Reformer):
- Characteristics : Focused on improvement and harmony, rigorous, conscientious, and idealistic.
- Motivations : Seeking perfection, doing what is right, correcting what is wrong.
- Fears : Criticism, falling short, imperfection.
- Tendencies : Strong sense of duty, self-discipline, tendency to be critical of oneself and others.
- Type 2 – The Helper (or the Caregiver):
- Characteristics : Altruistic, caring, empathetic, seeking to help others.
- Motivations : Being loved and accepted, feeling needed, helping others.
- Fears : Rejection, feeling useless, lack of recognition.
- Tendencies : Making sacrifices for others, being sensitive to others’ needs, seeking affection and approval.
- Type 3 – The Achiever (or the Performer):
- Characteristics : Ambitious, goal-oriented, success and image-driven.
- Motivations : Achieving success, being admired, being productive and efficient.
- Fears : Failure, inefficiency, not being valued.
- Tendencies : Commitment to success, competitiveness, significant concern for image.
- Type 4 – The Individualist (or the Romantic):
- Characteristics : Sensitive, creative, seeking identity and uniqueness.
- Motivations : Being unique, authentic, expressing deep emotions.
- Fears : Banality, not being understood, being ordinary.
- Tendencies : Expressing feelings, being artistic, seeking depth and meaning.
- Type 5 – The Investigator (or the Observer):
- Characteristics : Knowledge seeker, analytical, observer.
- Motivations : Understanding the world, accumulating knowledge, feeling competent.
- Fears : Ignorance, incompetence, being intruded upon.
- Tendencies : Observer, reserve, constant pursuit of understanding.
- Type 6 – The Loyalist (or the Skeptic):
- Characteristics : Reliable, loyal, vigilant in the face of danger.
- Motivations : Seeking security, anticipating problems, feeling supported.
- Fears : Insecurity, unpredictability, abandonment.
- Tendencies : Loyalty, concern for security, tendency to be skeptical and anticipate potential dangers.
- Type 7 – The Enthusiast (or the Optimist):
- Characteristics : Enthusiastic, adventurous, seeking pleasure and escape.
- Motivations : Avoiding pain, seeking pleasure, exploring new possibilities.
- Fears : Boredom, deprivation, being limited.
- Tendencies : Optimism, desire for adventure, tendency to flee from pain and seek stimulating experiences.
- Type 8 – The Challenger (or the Leader):
- Characteristics : Powerful, direct, protective, determined.
- Motivations : Controlling the environment, avoiding weakness, protecting the vulnerable.
- Fears : Vulnerability, being controlled by others, injustice.
- Tendencies : Leadership, protecting others, self-assertion.
- Type 9 – The Peacemaker (or the Mediator):
- Characteristics : Peaceful, harmonious, seeking unity.
- Motivations : Avoiding conflicts, maintaining peace, finding harmony.
- Fears : Separation, disharmony, conflict.
- Tendencies : Facilitating, seeking consensus, tendency to avoid confrontations.
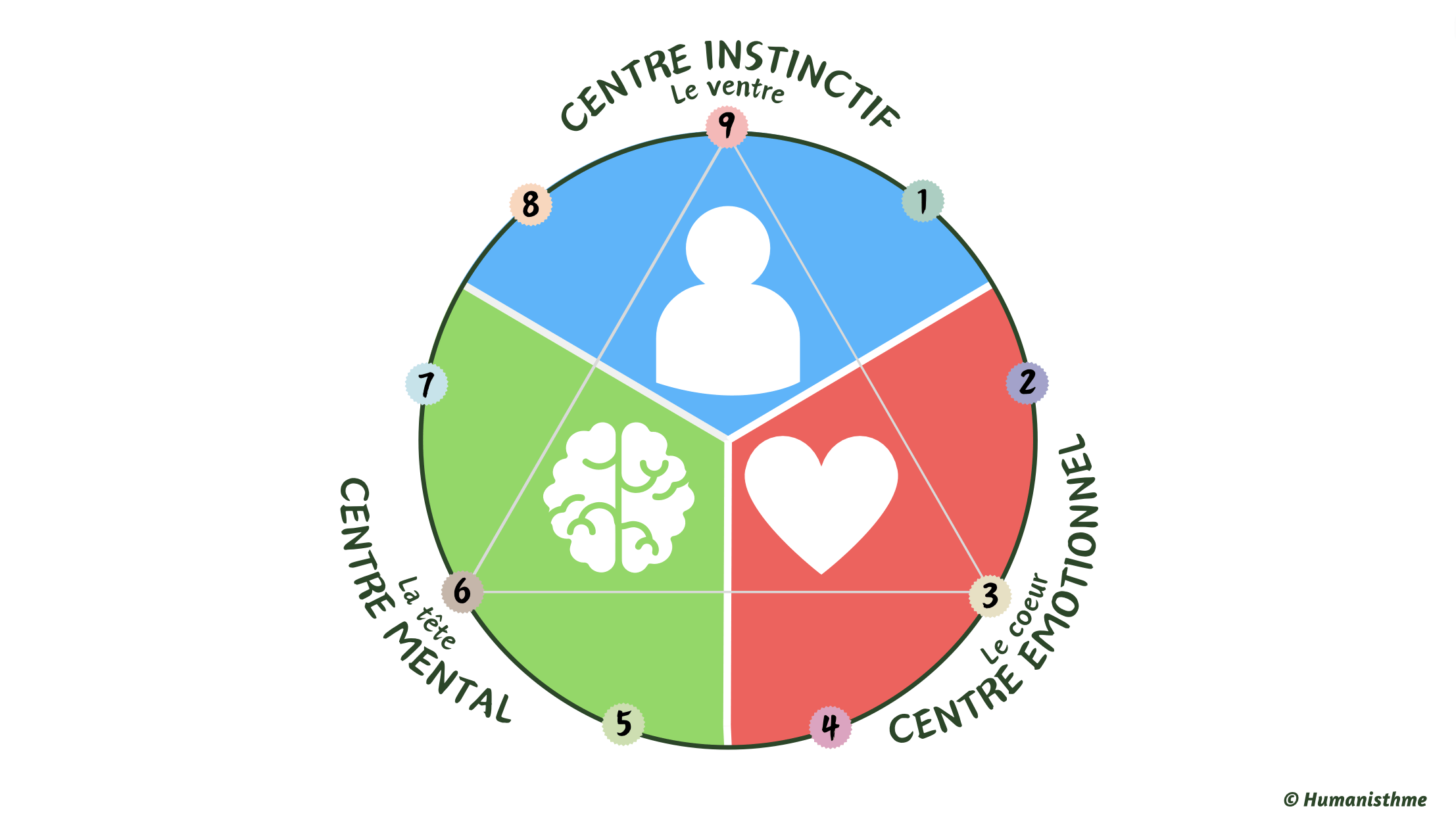
The three “centers” of the Enneagram refer to the three main domains of experience and functioning in human nature. Each of these centers represents a sphere of operation where individuals process, interpret, and react to their experiences.
1. Instinctive Center (or Body):
- Includes personality types 8, 9, and 1 in this center.
- Refers to instinctive reactions, physical needs, and basic impulses.
- Where immediate responses to environmental stimuli are processed.
- Manages responses related to survival, security, and self-preservation.
- Involves primary instincts of preservation, self-preservation, and seeking physical security.
2. Emotional Center (or Heart):
- Includes personality types 2, 3, and 4 in this center.
- Involved in processing emotions, feelings, and interpersonal relationships.
- Where emotional experiences are felt, interpreted, and expressed.
- Manages understanding relational dynamics and emotional connections.
- Involves the search for connection, harmony, and emotional validation.
3. Mental Center (or Head):
- Includes personality types 5, 6, and 7 in this center.
- Involved in processing information, rational thinking, and logic.
- Where ideas, concepts, and problems are analyzed and resolved.
- Manages perception, understanding, and conceptualization of the world.
- Involves the search for understanding, clarity, and self-mastery through knowledge.
Each individual has a predominant center that influences their way of perceiving, reacting, and interacting with the surrounding world. However, the Enneagram model highlights that for balanced personal development, it’s essential to work on all three centers, integrating the instinctive, emotional, and mental aspects of personality to achieve overall growth and harmony.
The arrows and connection lines in the Enneagram represent the interactions and relationships between different personality types. They show how one type may react or behave under the influence of another type, highlighting movements toward healthier or less healthy behaviors.
- Growth Arrows:
- Each type has an arrow pointing to another type when that first type is in a positive or growth state.
- When an individual feels secure and balanced, they may adopt certain characteristics of the type their growth arrow points to.
- This means that in times of personal growth, a person might adopt positive qualities from another type, aiding in handling situations and challenges better.
- Stress Arrows:
- Each type also has an arrow pointing to another type when that first type is in a stressed or insecure state.
- During stress or when the individual is unbalanced, they may adopt negative or less healthy traits from the type their stress arrow points to.
- This shows how an individual might react less favorably under pressure, adopting behaviors or attitudes associated with another type during times of tension or stress.
- Connection Lines:
- In addition to growth and stress arrows, there are lines directly connecting types to each other.
- These lines represent relationships between different types and show how these types interact and influence each other in normal or daily circumstances.
- For instance, one type may have a direct connection with another type, indicating they share some similarities or may understand each other more easily, while other types may have more tense or conflicting relationships.
Therefore, the arrows and connection lines in the Enneagram help understand how personality types interact and how an individual can evolve towards healthier or less healthy behaviors based on their emotional state and stress level. These connections symbolize the complex dynamics of human relationships and reactions to life’s challenges.
The Enneagram allows me to…
Need examples to visualize these Enneatypes? No problem, here are some examples of real people and fictional characters corresponding to each Enneagram type:
- Type 1 – The Perfectionist:
- Real : Michelle Obama | Nelson Mandela
- Fictional : Hermione Granger (Harry Potter) | Tintin (The Adventures of Tintin)
- Type 2 – The Helper:
- Real : Elvis Presley | Simone Veil
- Fictional : Daenerys Targaryen (Game of Thrones) | Anakin Skywalker (Star Wars)
- Type 3 – The Achiever:
- Real : Dwayne Johnson (The Rock) | Thomas Pesquet
- Fictional : Iron Man / Tony Stark (Marvel) | Patrick Jane (The Mentalist)
- Type 4 – The Individualist:
- Real : Lady Gaga | Edith Piaf
- Fictional : The Mad Hatter (Alice in Wonderland) | Raj Koothrappali (The Big Bang Theory)
- Type 5 – The Investigator:
- Real : Bill Gates | Marie Curie
- Fictional : Sherlock Holmes (Sherlock) | Egon Spengler (Ghostbusters)
- Type 6 – The Loyalist:
- Real : Eminem | Stromae
- Fictional : Chandler Bing (Friends) | Batman (Batman vs Superman)
- Type 7 – The Enthusiast:
- Real : Walt Disney | Jean Dujardin
- Fictional : John Hammond (Jurassic Park) | Peter Quill (Guardians of the Galaxy)
- Type 8 – The Challenger:
- Real : Martin Luther King Jr. | Jean-Luc Mélenchon
- Fictional : Katniss Everdeen (Hunger Games) | James Bond (James Bond – Daniel Craig)
- Type 9 – The Peacemaker:
- Real : Abraham Lincoln | François Hollande
- Fictional : William Byers (Stranger Things) | Obelix (Asterix)
